Raghad Alotaibi

This portfolio showcases the data science projects I've recently completed by using machine learning algorithms to various business and real-world problems through computer programming languages including Python and R.
Check My Articles on Medium.com
View My LinkedIn Profile
Identifying Factors Involved in Road Accident Using Data Mining Techniques
A team project conducted to identify the factors that are involved in road accidents in the United Kingdom
Abstract car accidents are considered a serious issue in every country, especially when the cars are usually considered the main transportation method. It costs the lives of the drivers, passengers and pedestrians. In this project, a study was conducted to investigate which factors are the main cause of car accidents severity using the UK car accidents’ dataset. Feature selection process was applied using the random forest to get the features’ importance, along with the association rules. The methods used in the study were the decision tree and the random forest as the learning models to predict the accident severity. Furthermore, to enhance the results these learning models were applied in collaboration with AdaBoost to increase the metrics’ results, where the best model gained an accuracy of 84.95%. These models were applied after balancing the dataset to remove the unbiased case in the targeted feature.
Introduction Road accidents are a global serious threat, as it results in severe injuries, disabilities and it even costs peoples their lives. According to World Health Organization (WHO) global status report on road safety in 2018 reported that road accidents causes more than 1.35 million deaths each year and up to 50 million injuries. Therefore, mitigating these accidents is an important area to look into. The main purpose of this study is to address the severity of the accidents, and what is the cause of such accidents to be severe. In general, the severity of accidents can be categorized into accidents with slight, serious and fatal damage to the people involved.
In order to provide effective solution to the addressed problem, there were two main issues needed to be confronted: unbalanced data classes for the independent variable, and feature selection due to the huge number of features in the dataset, and to select which of the features are the main factors to affect the accidents’ severity.
Data description
In this study the UK accidents dataset afforded by Kaggle is used. it provides detailed traffic data about road accident from 2005 to 2014. This data is a 10 years historical data divided into three datasets: accident, vehicles and casualties’ datasets each of which are at the size of 1.6m, 2,2m and 3m records respectively. The aim of this study is to investigate the most important factors that affects an accident severity using data mining and data analytics techniques. The objective of this workis to assess the performance of the learning models after balancing the data.
The accident’s dataset contains the general information of an accident such as: accident severity, weather, location, date, hour, day of the week, road type…etc. Whereas, the Vehicle dataset describes the vehicle conditions which was involved in the accident like the vehicle type, model, engine size, driver sex, driver age, car age…etc. The third dataset which is the casualty dataset has the information of the people involved in the accident such as the severity of the causality’s condition, their age, sex social class, casualty type, pedestrian or car passenger.
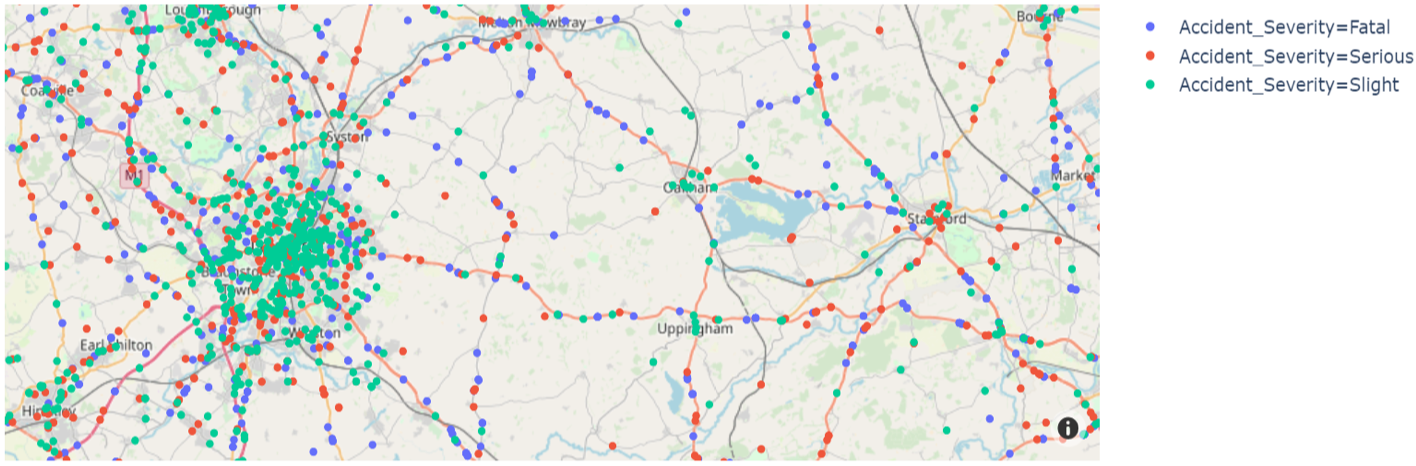
The following figure shows the distribution of the accidents color coded by their severities. The fatal and serious accidents happens mostly on highways and the Cities and villages have a high ratio of slight accidents.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
In this study, we are interested in finding the cause and which factors of the accidents and what causes the severity to vary from accidents to another. Therefore, the vehicle dataset was considered as a source out of the context of this study and would not be considered in this scope. After that, the accidents and casualty datasets are merged by the accident index feature which works as a unique identification to each accident. The merge of these two datasets have resulted in gaining 46 attributes and 2216720 records as a final dataset. The dataset was explored and assessed by using the library pandas_profiling which in return performs basic analysis to give more valuable information about the data. The following figure illustrates a basic overview on the dataset, as well as the missing values and high correlated variables. This profiling works as a data assessing report which highlights the major issues to be found within the data, which leads to which cleaning techniques to be followed.

Data Cleaning
After the dataset has been assessed and the issues were found, they were cleaned and fixed using both pandas and numpy packages, where the data types were changed from integers to objects. Some of the attributes were deleted due to multiple reasons, such as high correlation between two attributes which results in features overlapping, like “age band, location northing, location easting”. High missing value percentage and some attributes referring to IDs were deleted as well. Age attribute had some missing values which was replaced with the median to fill in the gap in the dataset. Some attributes had the value “unknown” such as: road type, weather, pedestrian location and pedestrian movement, which does not have much importance in the analysis. Therefore, these unknown values were deleted.
Data Balancing
Unbalanced data is one of the main drawbacks occurring in the previous works which they did not provide solutions for it. Numerous studies in similar fields were applied, but there was no balancing to the afforded data which in result presents a serious lack of consistency in their model’s metrics. For this reason, the delivered study proposes a balancing approach to improve the model’s results. RandomUnderSampler function from python was used in order to randomly under sample the dominant classes which are the slight and serious classes based on the fatal class stored in the target attribute (Accident_Severity).
Feature Selection
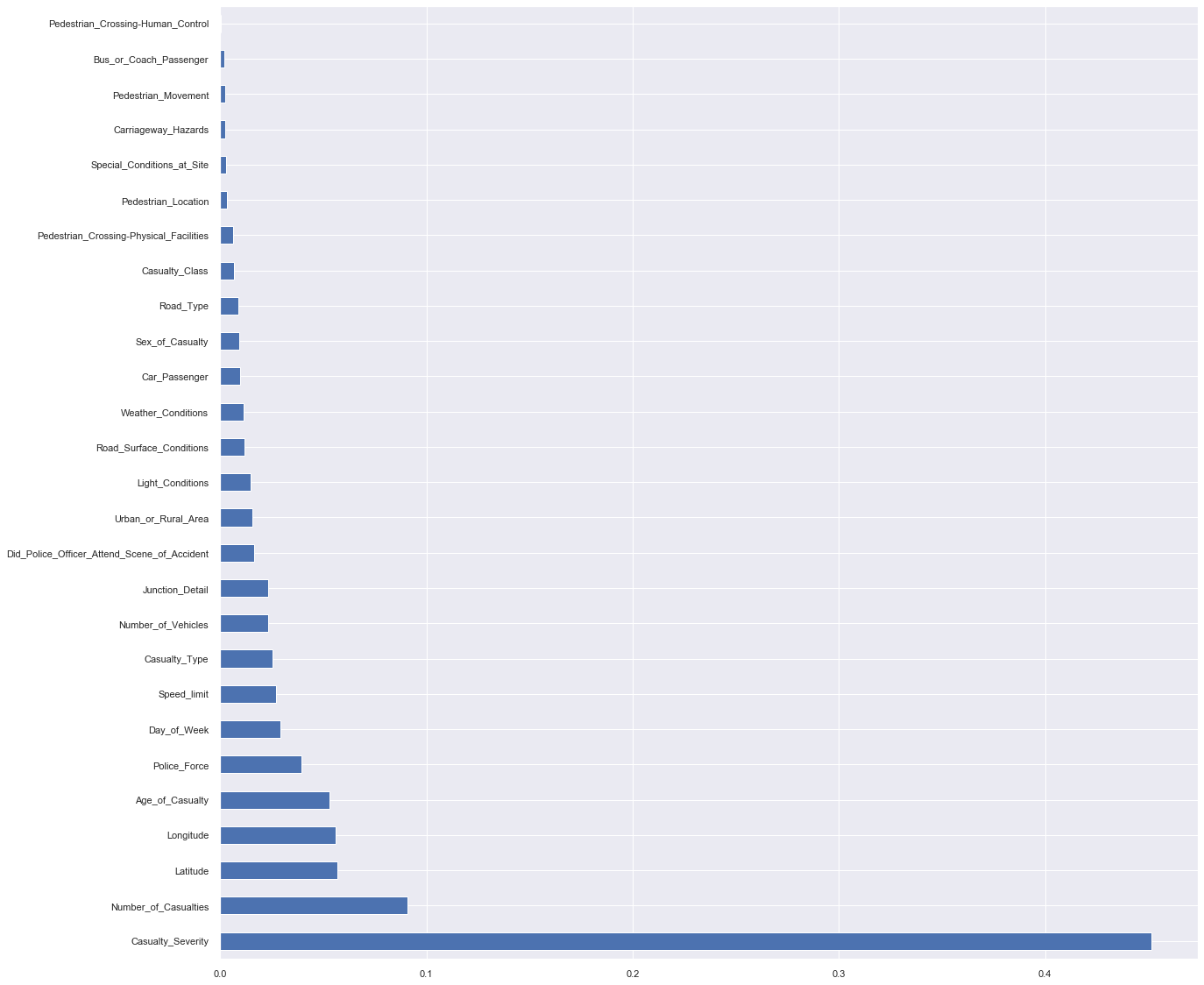
The learning models which have produced the highest results based on the previous studies were both the decision tree and the random forest. Upon the authors’ findings, it was considered to use the same models with more enhancement to raise the acquired results. This was achieved by first applying features selection using the random forest algorithm, where it returned the importance degree of each feature with respect to its effect on the accident severity. As shown in following figure, the threshold of the selected features was specified at the value of: (0.023385).
Data Modeling
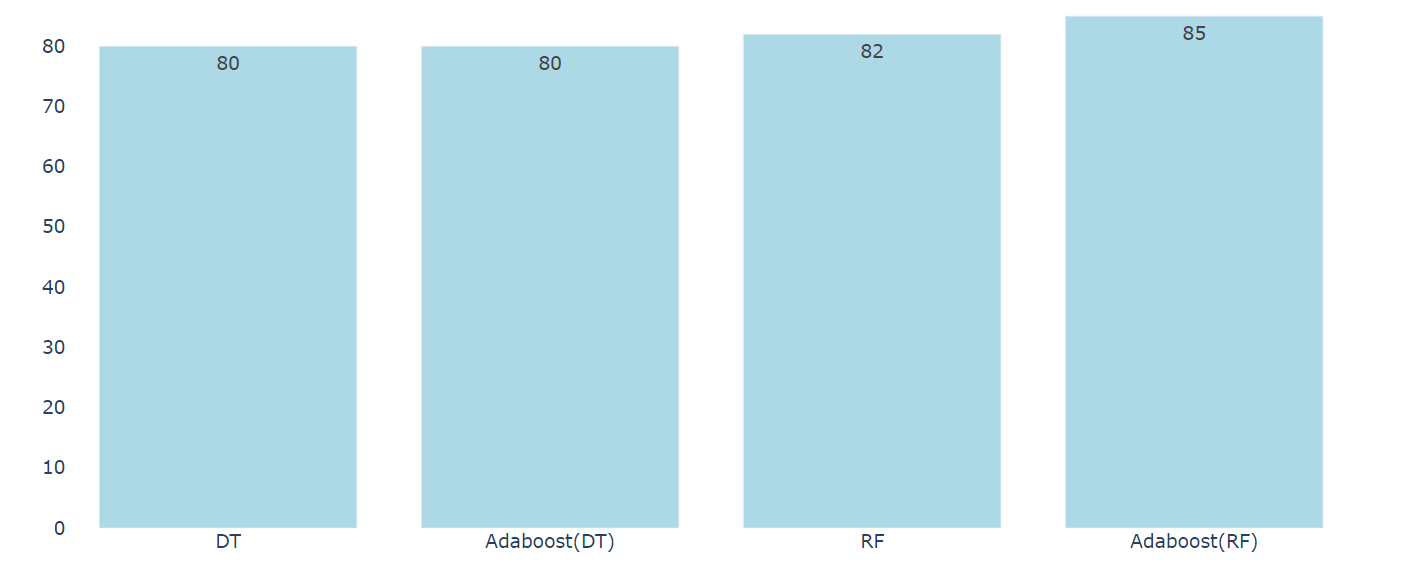
After selecting the features and balancing the classes of the independent variable, the machine learning algorithm were applied on the data. Two learning models were selected to apply and test the results, which are the DT and RF. The dataset was divided as 30% and 70% for the testing and training sets respectively. The model was applied on the balanced data with the selected features which has the highest importance values. Moreover, to enhance the results of the models we used AdaBoost model with the DT and RF classifiers. Using AdaBoost in collaboration with the learning models has paid off in increasing the learning metrics, and exceeded to give the learning models the consistency of the metrics’ values.
Class Association Rule (CAR)
NOTE: this part of the project was done by me, for the source code click here
Further investigation on the factors that indicates the fatal casualty severity class of accidents was conducted by using the class association rule in R programming language. 18 attributes from the merged and balanced dataset were used to generate 65 rules with casualty severity fatal class in the consequent. The numerical attributes were discretized to intervals for example age, speed limit, number of vehicles and number of casualties and the date and time were converted to seasons and parts of the day (morning, evening and night).
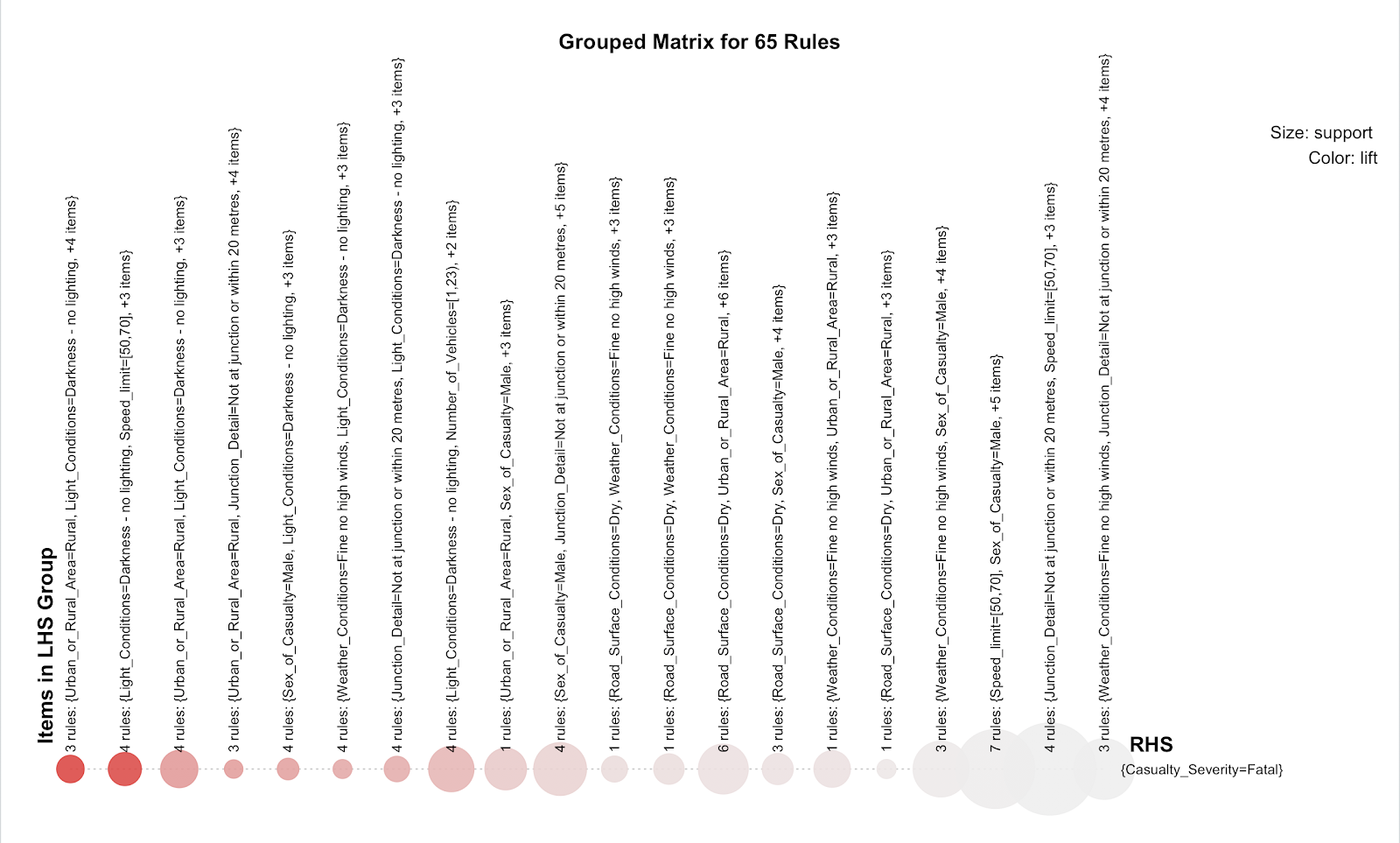
It is noticeable that most fatal casualties happened to male pedestrians with no lighting conditions and with numbers of casualties between 1-24 including 1-23 number of vehicles in the accident in rural areas. Evidently, the drivers did not obey the legal speed limit of the road, leading to fatal injuries with little to no impact of the weather and road surface conditions.
Results
In this study, different data mining models have been used in order to identify the most influential factors that affected the accident severity. The data was first balanced in order to omit any biased information that may occur in the learning process, as it was clear that the slight damage class in the dataset has the highest value which resemble up to 90% of the dataset. For this reason, it was a mandatory step to balance the data at first before applying any machine learning models. After the resolvement of the first obstacle, the features were selected based on their highest importance results. These features were considered as the features with the highest effect on the class of the independent variable. Adding AdaBoost to the DT and RF learning models has given stability in the acquired results.
Combining AdaBoost model with the RF classifier has provided the highest results in the tested models with the accuracy of 84.95%. In previous studies, the authors provided high accuracy results regardless of unbiased information in the dataset, while in this study the consistency of the provided results was the priority to be achieved.
Conclusion
After applying the learning models on the balanced dataset, it was apparent that the provided metrics results had consistency which shows the reliability of the model to give accurate results for this study. In addition to that, the feature selection method had given the top factors that affect the severity of the accidents. These features were tested using the RF and DT learning models where the high and stable results have concluded the effectiveness of balancing the data and the accuracy of the selected features by the algorithm.